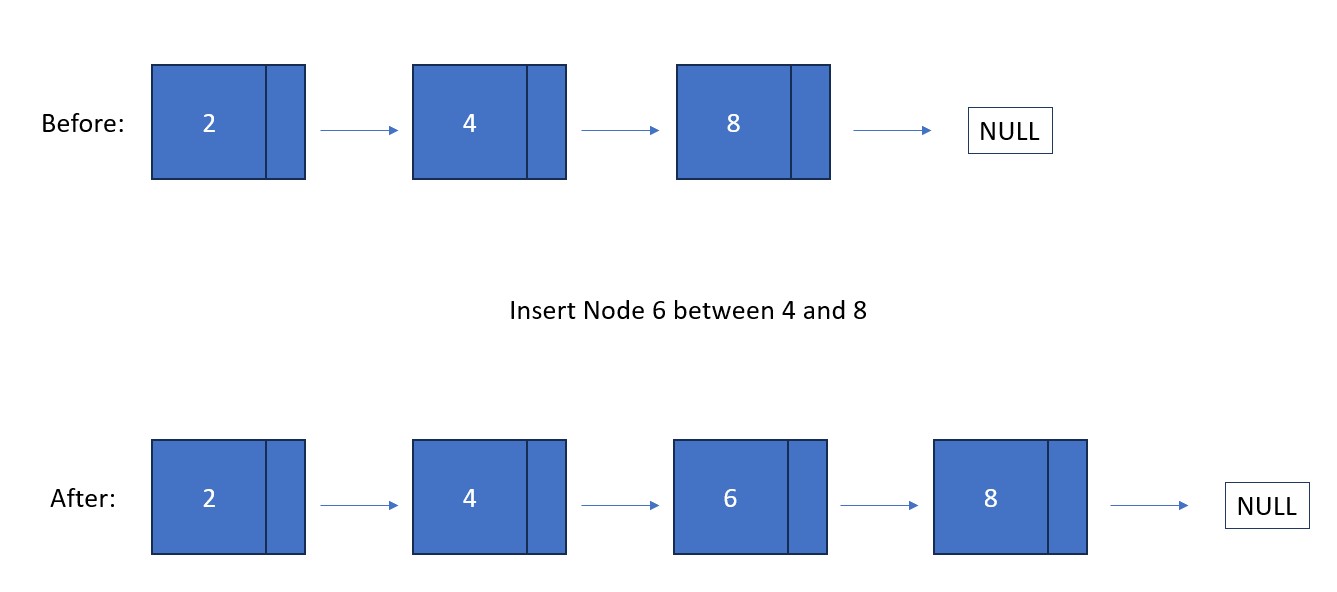
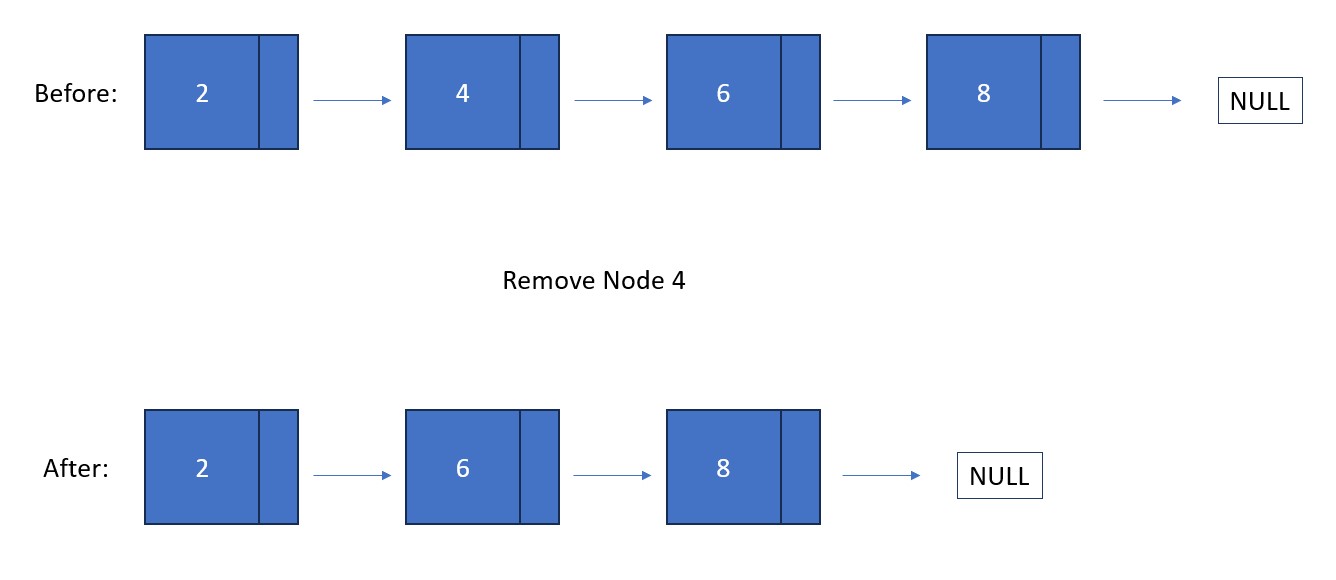
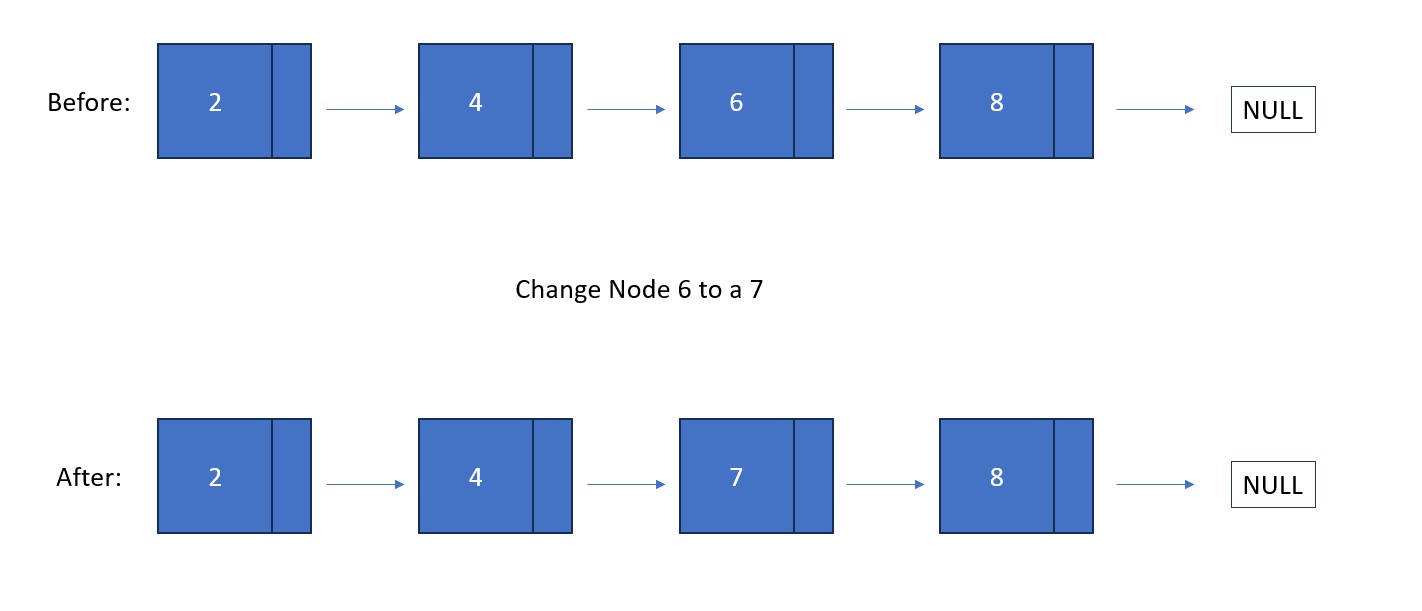
Fun Fact #1: Unlike in a
graph, a node in a Linked List consists of the data AND the arrow(s) stemming from it
(but not the ones pointing towards it).
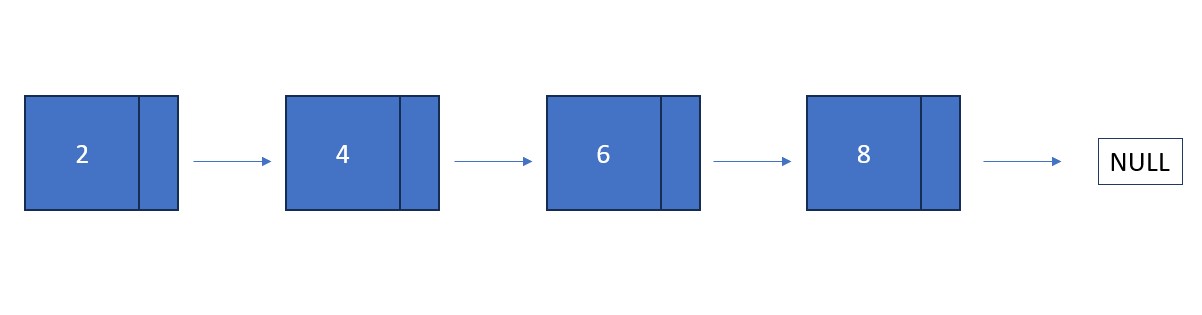
Fun Fact #2: In a singly
linked list, the tail node points towards "null" (meaning empty) to signify the end of the Linked List. This
is necessary because searching a Linked List is done by following the "arrows" node by node (much slower than
in an array) and without "null", there is no instruction for the search to stop once it reaches the final
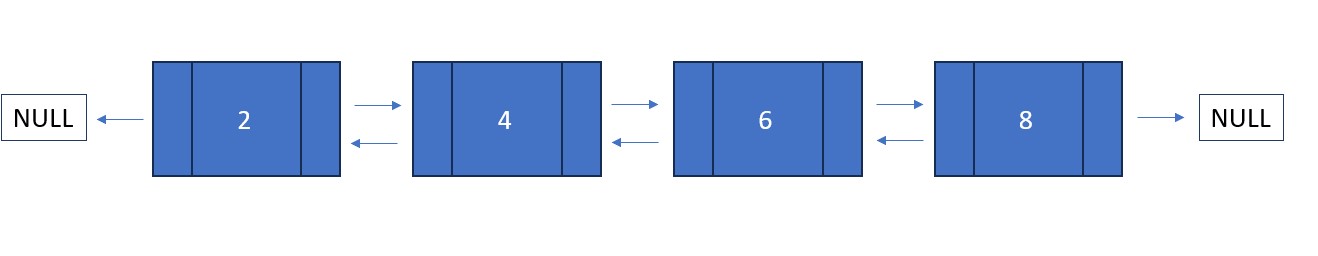
node. The same goes for doubly linked lists except a "null" value is pointed to by the tail AND the head.